Sustainable Finance
Overview of the Sustainable Finance
Hoshino Resorts REIT, Inc. (HRR) and Hoshino Resort Asset Management Co., Ltd. (Asset Management Company) believe that it is important to maximize investor value through ESG-conscious investment and asset management to improve the sustainability of HRR. Based on this belief, HRR has developed a framework as part of its efforts toward sustainability and is raising funds through sustainable finance.
It will not stop with fundraising by the issuing of sustainable finance, but will continue to contribute to the future through distinctive investment and asset management as it achieves its goal of creating shared value (CSV) aimed at solving social issues in accordance with its sustainability policy.
Sustainable finance is a collective term referring to the following. Please see each tab for details.
- Sustainability Finance (sustainability loans, sustainability bonds)
- Green Finance (green loans, green bonds)
- Positive impact finance (PIF)
- Blue loans
- Sustainability-Linked Loan (SLL)
Overview of Sustainable Finance Fundraising (As of November 28, 2025)
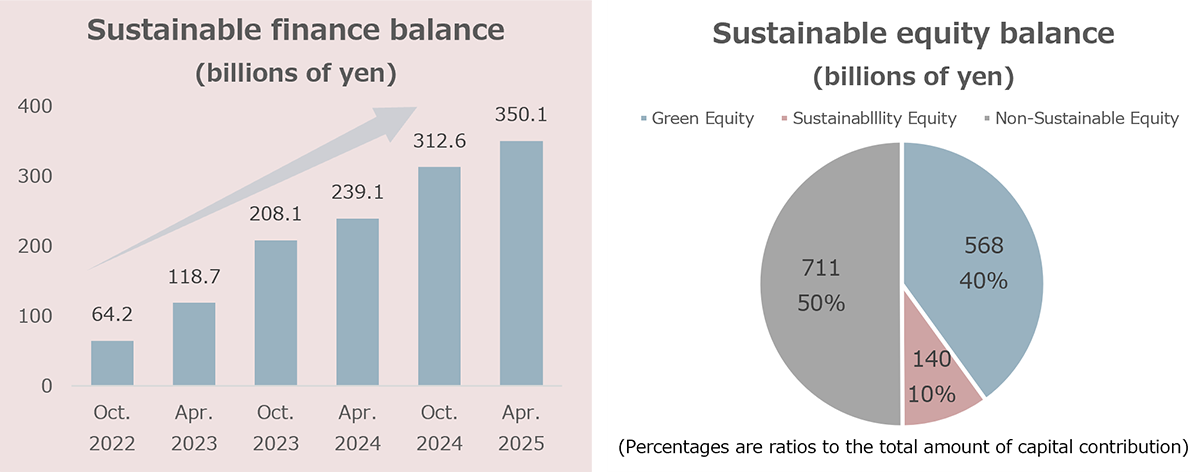
- The “Sustainable Finance Balance” includes green and sustainability finance executed under the former Green and Sustainability Finance Framework (prior to the update in September 2024).
- The “Green Equity Balance” and the “Sustainable Equity Balance” are calculated based on the criteria in effect at the time the relevant environmental certifications were obtained, regardless of any subsequent changes to the certification systems.
